High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer made from the monomer ethylene. Known for its high strength-to-density ratio, HDPE is one of the most widely used plastics in various industries today. It is characterized by its rigidity, chemical resistance, and low moisture absorption, making it suitable for a diverse range of applications.
HDPE is produced through the polymerization of ethylene gas, which occurs primarily via two processes:
- Ziegler-Natta Catalytic Polymerization: This low-pressure process utilizes a catalyst, allowing for the creation of HDPE with a narrow molecular weight distribution
- Gas Phase Polymerization: In this method, ethylene is polymerized in a gas phase reactor using specific temperature and pressure conditions.
Important Characteristics of HDPE
- Density: The density of HDPE typically ranges from 0.93 to 0.97 g/cm³.
- Melt Flow Index (MFI): A typical MFI for HDPE can range from 0.2 to over 10 g/10 min, depending on the molecular weight.
- Tensile Strength: HDPE can have a tensile strength of up to 37 MPa (megapascals).
- Chemical Resistance: Resists acids, alcohols, and hydrocarbons but may be affected by strong oxidizers.
Grades of HDPE and their application
- HDPE 1200 (or HDPE 2): HDPE 1200 is widely used for manufacturing milk jugs, detergent bottles, and yogurt containers.
- HDPE 1500: Used for applications requiring increased impact resistance, such as toys and household products.
- HDPE 2000: Known for its high molecular weight and used in more advanced applications like piping and water supply systems, industrial containers and construction.
Transportation and storage of HDPE
HDPE should be transported and stored in clean, dry, and shaded environments to prevent degradation from UV light and temperature extremes. The following are common ways to transport HDPE.
Container Ships: For large quantities of polyethylene, container ships are one of the most common methods of transport.
Tanker Trucks: For domestic transportation or shorter distances, tanker trucks are used to transport polyethylene in bulk, especially if it’s in liquid form or granules.
Flatbed Trucks: These can be used for transporting polyethylene in bulk bags (jumbo bags) or in other large packaging forms.
Air Freight: For small quantities that need to be delivered quickly, air transport can be an option, though it is generally more expensive than other methods.
Rail Freight: In regions with developed rail infrastructure, rail freight can be a cost-effective means for transporting large quantities of polyethylene.
Packaging of HDPE
HDPE is typically packaged in specific ways for sale and distribution. Common packaging methods include:
Multi-layer Bags: Heavy-duty polyethylene is often packaged in large bags (jumbo bags) or smaller bags. These bags are usually made from polypropylene or similar materials and are designed for easy transportation.
Barrel Packaging: For smaller quantities, polyethylene is also packaged in plastic or metal barrels.
Pallets: Bagged or barreled packages are typically placed on pallets to facilitate easier transportation and storage.
Bulk Packaging: In some cases, heavy-duty polyethylene is transported in bulk and without packaging in large tankers or containers.
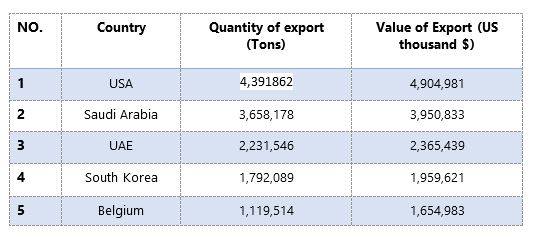
Top Exporter countries based on 2023
Major Exporter of HDPE include : USA, Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Korea and Belgium .
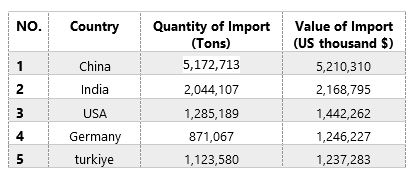
Top Importing Countries based on 2023
Major importer of HDPE include : China, India, USA, Germany and Turkey
Safety, Dangers, and Risks of HDPE
HDPE is recognized as safe for food-related applications. However, during its manufacturing, processing, or burning, it can release hazardous substances, including dioxins. It is important to adhere to safety regulations to mitigate these risks, using personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling raw materials or in production.
Price and Effective Parameters on Price
Price fluctuations in HDPE are influenced by factors such as crude oil prices, processing technology, supply-demand dynamics, and geographical location. The price can range from 0.900 to1.600 $ per kg, depending on current market conditions.
Important Websites and Magazines
If you need more information about HDPE, including prices, market trends, companies, and more, you can visit the following websites.”
- Websites:
- Resin Identification Codes (www.plastics.americanchemistry.com)
- Plastics Europe (www.plasticseurope.org)
- Society of the Plastics Industry (www.societyofplasticsindustry.org)
- Magazines:
- Plastics News
- Plastics Today
- Injection Molding Magazine
We hope you find this article helpful. For more information, please feel free to contact us..










